RPSC RAS 2026 Subject Wise Exam Pattern for Prelims, Mains & Interview Details
- >
- RAS Preparation Resources
- >
- Soils of Rajasthan
Soils of Rajasthan

Get in Touch with RASonly!

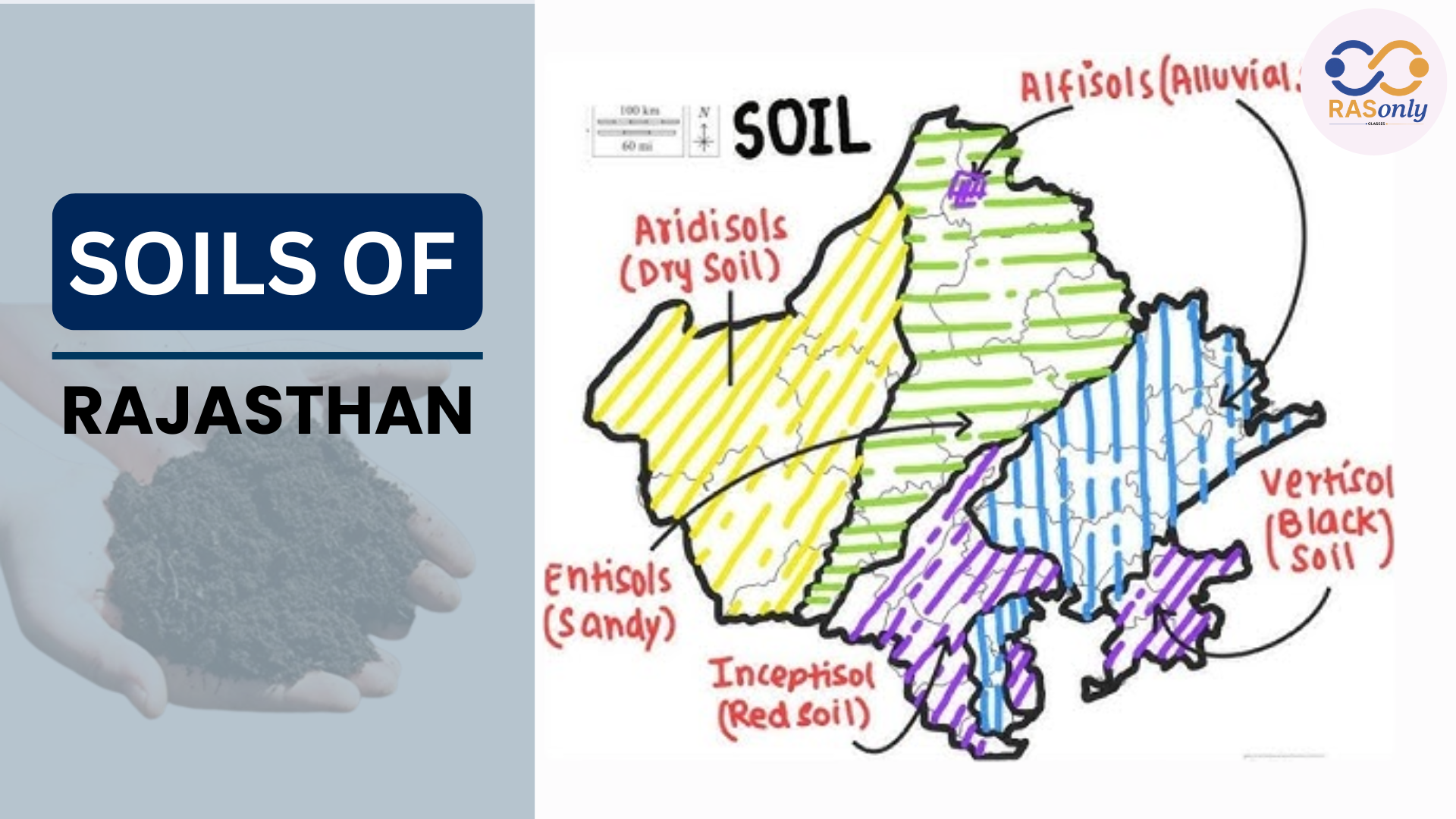
Because of variance in climatic and terrain in Rajasthan, the soil types vary widely in the state. There are major soil Types which are desert soil, red loamy soil, black soil, alluvial soil. Western Rajasthan consists of desert soil whereas there is alluvial soil in the eastern plain. In the southern districts there is black soil where they farm cotton. These soils vary in fertility and also determine the farming activities in the region.
Key points for RAS Mains
What are soils?
- Soil is the surface part of the earth surface that is made out of the rock breakup.
- It is very important in the areas of agriculture, forestry and biodiversity.
- It is made of minerals, organic matter, air, and water on top of which terrestrial ecosystems revolve, supporting the development of plants.
Soil Classification
- National-Level Classification:
- The Indian system divides its soils into 8 broad groups with 27 subtypes with the help of which suitability pertaining to agriculture and land management is identified.
- Rajasthan’s Classification:
- Diversity in climate (arid to semi-arid) in Rajasthan leads to varied soil profile.
- State Agriculture Department Classification: 14 unique types on the basis of region.
- USDA Scientific Classification:
- There are 5 major soil types; this classification is based on the properties of the soil aspects such as; texture, formation etc.
Institutions:
- ICAR (1929, New Delhi): First in soil research in India.
- USDA (1862, USA): Establishes international criteria of the soil classification.
Soil Types by Rajasthan Agriculture Department
| Region | Soil Types |
|---|---|
| Shri Ganganagar | Sie Rozems, Reverina |
| Bikaner | Gypsiferrous |
| Ajmer-Bhilwara | Calcie Brown Desert Soil, Non-Calcie Brown, New Brown Soil |
| Udaipur | Hilly Soil |
| Kota | Red Loam |
| Jaisalmer, Bikaner, Barmer | Desert Soil, Desert Dunes Soil |
| Alwar, Bharatpur, Karauli | New Alluvial Soil |
| Rajsamand, Ajmer | Yellow-Brown Soil |
| Pali, Jalore, Sirohi | Gray Brown Alluvial Soil |
| Kota, Baran, Bundi | Medium Deep Black Soil |
USDA Scientific Soil Classification in Rajasthan
| Soil Type | Regions Covered | Climate | Features & Crops |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aridisol | Bikaner, Jaisalmer, Barmer, Jodhpur | Extremely dry | High calcium, supports bajra, millet |
| Entisol | West of Aravalli (Jaisalmer, Bikaner, Barmer) | Arid–semi-arid | Young, sandy soils; millet, gram |
| Alfisol | Eastern Rajasthan | Sub-humid | Fertile, used for wheat, barley |
| Inceptisol | Udaipur, Chittorgarh, Dungarpur, Pali, Rajsamand | Semi-humid | Moderately fertile; mixed cropping |
| Vertisol | Hadoti Region (Kota, Bundi, Baran, Jhalawar) | Humid | Clay-rich; cotton, soybean |
Various types of soil found at Rajasthan
1. Sandy Soil (Dry Soil)
- Site: Jaisalmer, Bikaner, Barmer, Jodhpur
- Characteristics: rough, bad water absorption, high calcium
- Crops: Bajra, Moong, Moth, Guar, Groundnut
2. Brown Sandy Soil
- Place: Luni Basin (Jalore, Pali, Nagaur, Ajmer, Sikar)
- Features: Erosion sandstone, phosphate rich
3. Saline Soil: Reh/Kallar salty soil
- Place: Barmer, Jalore, Sri Ganganagar and Hanumangarh
- Qualities: irrigation misuse: white salt crust
- Agricultural products: pomegranate, sugarcane
4. Alluvial Soil
- Jaipur, Dholpur, Karauli, Alwar, Bharatpur
- Attributes: Potash rich, fertile soil laid down by rivers
- Farm crops: Wheat, Mustard, Barley, Bajra
5. Red Loamy Soil
- Place: Banswara, Dungarpur, Pratapgarh, South Udaipur
- Characteristics: reddish because of iron oxide, well drained
- Agricultural products: Maize, Rice, Sugarcane
6. Black Soil (Regur/Volcanic)
- Place: Hadoti (Kota, Bundi, Jhalawar)
- Aspects: Gritty, moisturizing, clay-like
- Agriculture: Cotton, Soybean, Spices
7. Red-Black Soil
- Place: Pratapgarh, Jhalawar, Bhilwara
- Agricultural produces: Maize, Cotton and Opium
8. Red-Yellow Soil
- Place: Udaipur, Ajmer, Bhilwara, Chittor
- Features: iron rich, needs erosion control
Soil Problems in Rajasthan
1. Soil Erosion
- Causes: Caused by deforestation, overgrazing and over tilling
- Categories: Layer, Sheet, Gully erosion
- Remedies: Plantation of trees, fencing, bunding
2. Salinity
- Causes:: Excessive irrigation, inadequate drainage, capillary movement
- Solutions: Leaching, utilization of gypsum
- Jalore, Bikaner, Ganganagar
3. Waterlogging
- Causes: Over-irrigation, poor drainage
- Solution: Eucalyptus plantation, drip /sprinkler systems, solutions
4. Alkalinity
- pH Level:>8
- Causes: Sodium/calcium/magnesium high salts
- Remedies: Guar-drenching, Gypsum, Rock phosphate
5. Soil Degradation
- Causes: Overuse of fertilizers, monocropping
- Solutions: Organic farming, crop rotation
Conclusion
Rajasthan is the land of tremendous soil variation, ranging between nutrient deficient deserts to highly productive regur soil. This variability is confirmed by geography, climate as well as type of rock. There is a necessity of having the best land and water management to ensure that powerful agricultural outcomes are realized but natural resources must be preserved.
Post Category
- RAS Salary
- Result
- RAS Admit Card
- RAS Job
- RAS Cutoff
- Preparation Tips
- RAS Answer Key
- RAS Exam Analysis
- RAS Syllabus
- RAS Previous Year Papers
- RPSC RAS Exam Pattern
- RAS Interview
- RAS Mains Exam Date
- RAS Vacancy
- RAS Test Series
- RAS Best Books
- RAS Preparation Resources
- RAS Coaching Centre
- History
- Polity
- Geography
- Economics
- Science
- Art and Culture
- RPSC RAS Application Form
- RPSC RAS Notification
RASonly Interview Guidance Program

Mr. Ashok Jain
Ex-Chief Secretary Govt of Rajasthan
- IAS officer of the 1981 batch, Rajasthan cadre.
- Passionate about mentoring the next generation of RAS officers with real-world insights.
- Got retired in Dec 2017 from the post of Chief Secretary of the state of Rajasthan.

Mr. Guru Charan Rai
Ex-ASP / SP in Jaisalmer
- Guru Charan Rai, IPS (Retd), retired as Inspector General of Police (Security), Rajasthan, Jaipur in 2017.
- Served as ASP and SP in Jaisalmer, Nagaur, Sri Ganganagar, Sawai Madhopur, Dausa, Sikar, and Karauli.
- He also held key positions as DIGP and IGP in the Law and Order division.

Mr. Rakesh Verma
Ex-IAS Officer, B.Tech, MBA, and M.A. (Economics)
- IAS officer of the 1981 batch and retired in Chief Secretary Rank.
- Civil servant of high repute and vast experience.
- Has been teaching UPSC CSE subjects for the last six years.
Related Post
Daily Current Affairs for RAS Exam Preparation 2026

Rajasthan Pavilion Shines at Stone Mart Jaipur 2026
February 07, 2026
Rajasthan Achieves 3,000 MW Under PM-KUSUM Scheme
February 07, 2026
Gram Utthan Shivirs Strengthen Rural Governance in Rajasthan
February 07, 2026
Jaipur Badminton: 72-Minute U-15 Final Creates Record
February 06, 2026👉🏻 Register Today to Join Classes! 👍🏻
- Team RASOnly -
🎯 Benefits of RASOnly Coaching:
- ✅ 1:1 Mentorship with RAS Officers
- ✅ Experienced and Expert Faculty
- ✅ Free Library Access
- ✅ Daily Minimum 4 Hours Must
- ✅ Comprehensive Study Material
- ✅ Regular Tests & Performance Analysis
- ✅ Personalized Guidance & Doubt Solving
- ✅ Online & Offline Class Options
- ✅ Affordable Fees with Quality Education
Key Highlights:
- 👉🏻 3-Day Refund Policy
- 👉🏻 New Batch Starting from 04 August
- 👉🏻 Registration Amount: Only ₹1000









