RAS Training Period Details 2026: RPSC RAS Training Center, Duration, and Training Process
Horticulture | Definition, Types, Techniques, & Uses

Get in Touch with RASonly!

This article provides a comprehensive overview of horticulture in India, explaining its definition, branches, Major Crops, and modern techniques. It highlights the role of horticulture in enhancing farmers’ income, nutritional security, employment generation, and sustainable development, with special reference to administrative planning and Rajasthan’s agricultural priorities.

Horticulture holds a very strategic role in the Indian agricultural economy and rural development model. Horticulture is not only a subsector of agriculture but also a potent generator of income as well as nutritional security, employment, and sustainable development. Horticulture provides resilience and value creation opportunities to a high concentration of small and marginal farmers in a country where major changes in climate have escalated. To the administrators and policymakers, horticulture is a transition from subsistence agriculture to market-oriented agriculture of high value, which is consistent with the objective of inclusive growth and sustainable development.
Meaning of Horticulture in Administrative Context
Horticulture can be defined as the scientific production, processing, and sales of fruits, vegetables, flowers, plantation crops, spices, and medications plants and aromatic plants. Horticulture also deals with quality, productivity, management of perishability, and value addition, unlike cereal-based agriculture.
Governance-wise, horticulture:
- Increases income of farmers per unit of land.
- Enhances eating habits and diet.
- Essentially provides forward and back connections.
- Favors agri-processing and exports.
Significance of Horticulture in Indian Agriculture
Horticulture has emerged as one of the fastest-growing segments of Indian agriculture. It contributes significantly to agricultural GDP and employs millions in production, processing, logistics, and marketing.
Why Horticulture is Important for India
- High population and rising food demand
- Growing awareness of nutrition and health
- Fragmented landholdings
- Need for employment-intensive agriculture
- Climate change challenges to food grains
Key Horticulture Products of Rajasthan
Fruits and Vegetables

Branches of Horticulture
Branch-wise Classification
| Branch | Focus | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Pomology | Fruit crops | Mango, Citrus |
| Olericulture | Vegetables | Tomato, Cabbage |
| Floriculture | Flowers | Rose, Orchid |
| Plantation Crops | Commercial crops | Tea, Coffee |
| Spices & Condiments | Flavoring crops | Cardamom, Chilli |
| Medicinal Plants | Therapeutic crops | Ashwagandha |
This classification helps administrators in crop planning, extension services, and policy design.
Role of Horticulture in Farmers’ Income Enhancement
One of the core objectives of agricultural policy is doubling farmers’ income, and horticulture plays a central role in achieving this goal.
How Horticulture Increases Income
- Higher returns per hectare
- Short crop duration
- Multiple cropping possibilities
- Scope for processing and branding
- Export-oriented production
Comparison with Food Grain Crops
| Aspect | Food Grains | Horticulture |
|---|---|---|
| Income per hectare | Low to moderate | High |
| Value addition | Limited | Significant |
| Employment | Seasonal | Year-round |
| Market linkage | MSP-based | Market-driven |
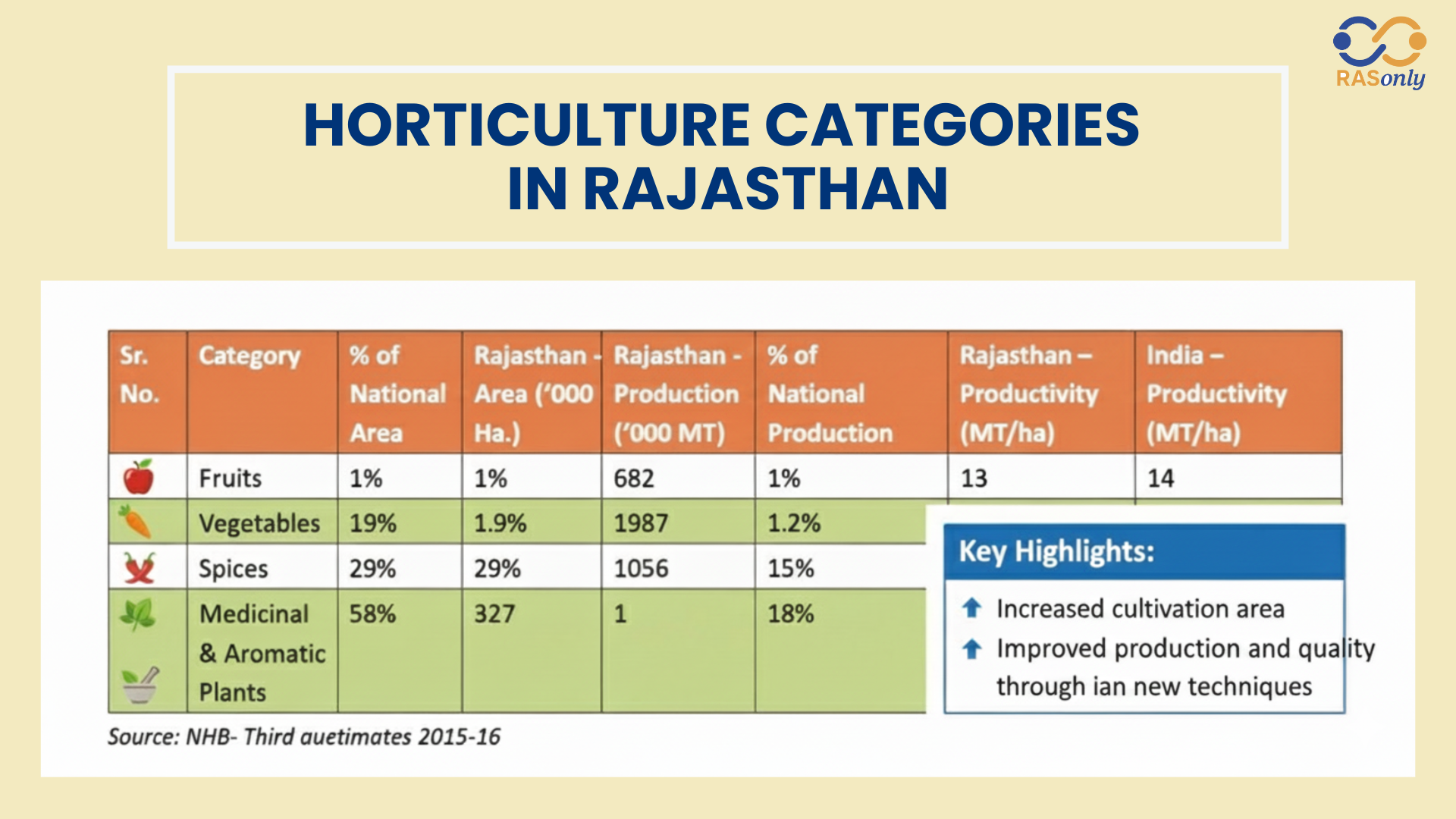
Horticulture and Nutritional Security
India faces the dual challenge of undernutrition and lifestyle diseases. Horticulture directly addresses this issue by ensuring availability of fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Administrative Importance
- Supports POSHAN Abhiyan goals
- Improves maternal and child health
- Reduces micronutrient deficiencies
- Enhances food diversity
Thus, horticulture is critical for achieving human development indicators.
Role of Horticulture in Employment Generation
Horticulture is labor-intensive and generates employment across the value chain.
Employment Areas
- Nursery development
- Cultivation and harvesting
- Post-harvest handling
- Cold storage and logistics
- Processing and marketing
This makes horticulture especially important for rural youth and women's empowerment.
Technology and Innovation in Horticulture
Modern horticulture relies heavily on technology to enhance productivity, reduce losses, and improve quality.
Key Technological Interventions
| Technology | Administrative Benefit |
|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Water efficiency |
| Polyhouse | Climate resilience |
| Tissue Culture | Disease-free planting |
| Cold Chain | Reduced wastage |
| Digital Marketing | Price discovery |
Technology adoption is essential for making horticulture competitive and sustainable.
Challenges in the Horticulture Sector
Despite its potential, horticulture faces several structural and operational challenges.
Major Challenges
- High post-harvest losses
- Inadequate cold storage
- Market price volatility
- Fragmented supply chains
- Climate change impacts
- Limited access to credit
To administrators, ensuring that these issues are tackled is a policy agenda.
Horticulture and Sustainable Development
Horticulture aligns well with the principles of sustainable development.
Sustainability Dimensions
- Economic: Higher income and diversification
- Social: Employment and inclusion
- Environmental: Efficient water use and biodiversity
Promotion of organic horticulture, integrated pest management, and water-saving technologies enhances sustainability.
Horticulture in the Context of Rajasthan
Rajasthan faces unique challenges such as arid climate, water scarcity, and regional imbalance. Horticulture offers solutions through crop diversification and efficient resource use.
Priority Areas for Rajasthan
| Focus Area | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Water conservation |
| Fruit Orchards | Income stability |
| Medicinal Plants | Dryland suitability |
| Date Palm & Aonla | Climate resilience |
| Floriculture | Urban markets |
Read More:- Types of Agriculture in India
Role of Government and Administration
Effective governance is crucial for horticulture development.
Key Administrative Responsibilities
- Policy formulation and planning
- Extension services and capacity building
- Infrastructure development
- Market reforms
- Monitoring and evaluation
Coordination between central, state, and local governments is essential.
Future Prospects of Horticulture
The future of horticulture is promising due to:
- Rising urban demand
- Health-conscious consumers
- Export opportunities
- Food processing growth
- Climate-resilient crop varieties
With proper planning and institutional support, horticulture can become a growth engine for Indian agriculture.
Conclusion
Horticulture is a strategic sector through which agriculture is connected to nutrition, employment, sustainability and economic growth. It focuses on the key problems, which include low agricultural earnings, malnutrition and climate change, as well as providing value addition and export.
To administrators, horticulture does not only concern the crop growing, it is also concerned with integrated rural development and inclusive growth. Policy support, adopting technology, and integrating into the market will enhance the strengthening of horticulture that will be instrumental in meeting the long-term development objectives of India.
Post Category
- RAS Salary
- Result
- RAS Admit Card
- RAS Job
- RAS Cutoff
- Preparation Tips
- RAS Answer Key
- RAS Exam Analysis
- RAS Syllabus
- RAS Previous Year Papers
- RPSC RAS Exam Pattern
- RAS Interview
- RAS Exam Date
- RAS Vacancy
- RAS Test Series
- RAS Best Books
- RAS Preparation Resources
- RAS Coaching Centre
- History
- Polity
- Geography
- Economics
- Science
- Art and Culture
- RPSC RAS Application Form
- RPSC RAS Notification
- RAS Eligibility Criteria
RASonly Interview Guidance Program

Mr. Ashok Jain
Ex-Chief Secretary Govt of Rajasthan
- IAS officer of the 1981 batch, Rajasthan cadre.
- Passionate about mentoring the next generation of RAS officers with real-world insights.
- Got retired in Dec 2017 from the post of Chief Secretary of the state of Rajasthan.

Mr. Guru Charan Rai
Ex-ASP / SP in Jaisalmer
- Guru Charan Rai, IPS (Retd), retired as Inspector General of Police (Security), Rajasthan, Jaipur in 2017.
- Served as ASP and SP in Jaisalmer, Nagaur, Sri Ganganagar, Sawai Madhopur, Dausa, Sikar, and Karauli.
- He also held key positions as DIGP and IGP in the Law and Order division.

Mr. Rakesh Verma
Ex-IAS Officer, B.Tech, MBA, and M.A. (Economics)
- IAS officer of the 1981 batch and retired in Chief Secretary Rank.
- Civil servant of high repute and vast experience.
- Has been teaching UPSC CSE subjects for the last six years.
Related Post
Daily Current Affairs for RAS Exam Preparation 2026

AIOC 2026 Conference: Boost to Eye Care and Health...
March 13, 2026
Rajasthan Assembly Seats May Rise to 270 After Delimitation
March 12, 2026👉🏻 Register Today to Join Classes! 👍🏻
- Team RASOnly -
🎯 Benefits of RASOnly Coaching:
- ✅ 1:1 Mentorship with RAS Officers
- ✅ Experienced and Expert Faculty
- ✅ Free Library Access
- ✅ Daily Minimum 4 Hours Must
- ✅ Comprehensive Study Material
- ✅ Regular Tests & Performance Analysis
- ✅ Personalized Guidance & Doubt Solving
- ✅ Online & Offline Class Options
- ✅ Affordable Fees with Quality Education
Key Highlights:
- 👉🏻 3-Day Refund Policy
- 👉🏻 New Batch Starting from 04 August
- 👉🏻 Registration Amount: Only ₹1000











