Rajasthan Tribes & Scheduled Areas – Constitutional Framework, Governance & Tribal Development for RAS 2026
Rajasthan Budget 2026–27 Summary for RAS 2026

Get in Touch with RASonly!

The Rajasthan Budget 2026–27 presents a fiscally disciplined yet growth-oriented roadmap aligned with “Viksit Rajasthan @2047,” emphasizing agriculture, infrastructure, social welfare, and green development. For RPSC RAS 2026 aspirants, it is a high-value topic linking fiscal policy, governance reforms, economic development, and sustainable growth.

The Rajasthan Budget 2026-27, presented on 11 Feb 2026 by Deputy Chief Minister and Finance Minister Diya Kumari in the State Legislative Assembly, outlined the state’s fiscal roadmap for the upcoming financial year. Being the third full budget of the Bhajan Lal Sharma government, it is targeted at the long-term development vision Viksi Rajasthan 2047, which entails inclusive growth, fiscal stability, capital investment, and sustainable economic growth. The budget incorporates the management of public finance, priorities of allocation in the sector and long term infrastructure planning, and keeping the fiscal deficit targets within responsible limits.
The budget is based on a balance that involves fiscal restraint and development priorities, with agriculture, infrastructural development, youth empowerment, healthcare, education, renewable energy, livelihoods in the rural areas, social security, and green projects taking center stage. It is accompanied by different new welfare initiatives for the farmers, women, youth,s and the marginalized groups.
This budget is important to RPSC RAS 2026 aspirants in terms of economics, governance, social development, fiscal policy, and environmental issues.
1. Budget at a Glance – Key Fiscal Figures
Rajasthan Budget 2026-27 indicates the balanced fiscal approach of the fiscal strategy, which is a mix of developmental expenditure, capital investment and fiscal discipline. The state has been pursuing an expansionary policy all along, keeping the fiscal deficit at sustainable levels under FRBM guidelines at a total outlay of more than 6 lakh crore. It focuses on the enhanced generation of revenues, the advancement of capital assets generation, and macroeconomic stability.
| Component | Amount / Details |
|---|---|
| Total Budget Size | ₹6.11 lakh crore (approx.) |
| Total Expenditure | ₹6.10 lakh crore (approx.) |
| Revenue Receipts | ₹3.25+ lakh crore (approx.) |
| Capital Receipts | ₹2.85 lakh crore (approx.) |
| Fiscal Deficit | ~₹79,000 crore (approx.) |
| Revenue Deficit | ~₹24,000 crore (approx.) |
Fiscal Context: The state is fiscally prudent and driving the development expenditure in other sectors. The size of the budget has increased over the past years, thus signifying an expansionary developmental position.
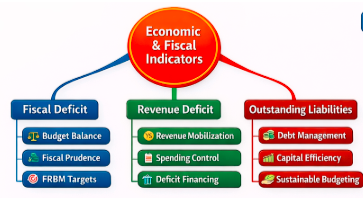
2. Economic & Fiscal Indicators
The Rajasthan Budget 202627 indicates slow fiscal consolidation with the prevailing developmental expenditure. Some of the macro indicators include better revenue management, decreasing fiscal deficit and manageable debt levels under FRBM discipline.
| Indicator | 2025–26 (RE) | 2026–27 (BE) |
|---|---|---|
| Fiscal Deficit (% of GSDP) | 3.87% | 3.69% |
| Revenue Deficit (% of Receipts) | -11.55 | -7.46 |
| Outstanding Liabilities (% of GSDP) | 37.99% | 36.80% |
RAS Analytical Takeaways:
- Fiscal deficit is gradually declining, showing improved budget balance.
- Revenue deficit reduction indicates better revenue mobilization and spending control.
- Outstanding liabilities remain high, necessitating prudent debt management.
This is pertinent directly when dealing with RAS questions of fiscal policy, public finance, FRBM targets and sustainable budgeting.
3. Major Revenue Sources
Rajasthan has a diversified revenue base which majorly relies on internal tax collection and central transfers. Increasing the personal tax base enhances financial independence and decreases reliance.
Revenue Composition
- Own Tax Revenue: ~₹1.62+ lakh crore
- State GST & Stamp Duty: Major contributors
- Excise Duty & Vehicle Tax: Important internal sources
- Share in Central Taxes: ~₹90,000 crore
- Union Grants & Central Assistance: ~₹44,000 crore
- Non-Tax Revenue: Mining royalties, petroleum rent, service charges
RAS Focus Areas: Tax buoyancy, GST performance, intergovernmental fiscal transfers, revenue diversification.

4. Agriculture & Farmers – Major Allocations
The economy of Rajasthan is still based on agriculture. The budget focuses on rural credit, irrigation systems, climate-resistant agriculture and livestock assistance.
| Agriculture Allocation Areas | Highlights |
|---|---|
| Farmer Loans & Credit | ₹25,000 crore support |
| Irrigation & Water Projects | ₹24,000+ crore works |
| Modern Farming | Solar pumps & green integration |
| Dairy & Livestock | ₹700 crore support |
| Crop Protection | ₹228 crore fencing infrastructure |
5. Health & Medical Sector Investments
The healthcare sector is still given a priority in terms of coverage of insurance, free medicines and improvements of the healthcare infrastructure. It is aimed at enhancing primary and tertiary healthcare provision.
Key Areas
- Expansion of public health insurance schemes
- Strengthening PHCs, CHCs, and district hospitals
- Medical college expansion
- Continued implementation of free medicine & diagnostic schemes
Exam Themes:
- Universal Health Coverage
- Public health infrastructure
- Right to health services (context of Right to Health Care Act 2022)
6. Education & Youth Empowerment
The budget encourages development of human capital by digital learning, skill development and higher education reforms.
Focus Areas
- Smart classrooms & digital infrastructure
- Technical and vocational education expansion
- Youth employability and skill ecosystem strengthening
RAS Link: Demographic dividend, knowledge economy, digital education reforms.
7. Green Budget & Environmental Initiatives
Green transition and strategies of climate action constitute a key pillar of the 2026-27 budget under environmental sustainability.
Key Measures
- Waste management infrastructure
- Carbon credit incentives for eco-friendly farming
- Promotion of green schools and environmental labs
- Renewable energy integration
Exam Link: Sustainable development, climate governance, green economy transition.
8. Social Sector Spending
The budget reinforces welfare governance by strengthening social security and targeted interventions for vulnerable sections.
A. Women, Children & Marginalized Groups
- Women's empowerment programs
- Nutrition & early childhood care initiatives
- Safety and skill development schemes
B. Pension & Social Security
- Support for the elderly and widows
- Expansion of welfare schemes for vulnerable communities
RAS Focus: Social justice, inclusive growth, welfare state model.
9. Infrastructure & Urban Development
The purpose of infrastructure development is to increase economic growth, connectivity, and tourism potential.
Key Highlights
- ₹3,427 crore allocation for infrastructure
- Tourism circuit development & heritage conservation
- Aero-city initiatives near regional airports
- Urban utilities & smart city expansion
Exam Relevance: Urban governance, infrastructure financing, tourism economy.
10. Policy & Governance Reforms
The budget enhances administrative changes in order to boost efficiency and services to citizens.
Key Reforms
- Simplification of vehicle registration taxes
- Judicial infrastructure strengthening
- Integrated skill centres for ex-servicemen
RAS Link: Governance reforms, administrative efficiency, citizen-centric policy design.
RAS Scorecard – Why Rajasthan Budget 2026 Matters
The Rajasthan Budget 2026-27 is the most essential to RPSC RAS Prelims, Mains, and Interview due to the abundance of questions based on its budgetary allocation in the Rajasthan Economy, Fiscal Policy, Governance, Agriculture, Social Justice, and Sustainable Development. The conceptual knowledge of budget magnitude, sectoral appropriations, fiscal deficit patterns, welfare schemes, and the Vision 2047 strategy reinforces both the accuracy of fact and the strategies of analysis in responses.
RAS Budget Relevance Scorecard
| RAS Stage | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Prelims (GK & Current Affairs) | Direct MCQs from budget size, fiscal deficit (% of GSDP), major sector allocations, agriculture & social sector spending, green initiatives. |
| Mains (GS I, II, III) | Applicable in responding to economic development, fiscal discipline, agriculture reforms, welfare state model, infrastructure growth, environment and green budgeting. |
| Interview (Personality Test) | Helps prove policy awareness, governance knowledge, fiscal prudence and long-term Vision Viksit Rajasthan 2047 vision. |
Key Exam Themes Linked to Budget 2026
- Fiscal Policy & FRBM Targets
- Revenue Mobilization & GST Performance
- Agriculture & Rural Development
- Health & Education Investment
- Women & Social Welfare Schemes
- Green Budget & Climate Action
- Infrastructure & Urban Development
To RAS Aspirants, the Rajasthan Budget 2026 is not a combination of numbers to memorize. It is to be interpreted as a policy document that represents the priorities of development of the state, the fiscal administration approach, and the inclusive growth plan.
Conclusion
This budget is prospective, visionary, and balanced, which would support sustainable development, human development, rural change, and environmental management, as demonstrated in the Rajasthan budget 2026-27. Though welfare is managed without compromising on fiscal stability, investments are made in the agricultural sector, health, education, infrastructure, green initiatives and social security.
For RAS Aspirants, the budget offers rich material for Prelims MCQs, Mains analytical answers, and Interview discussions - especially on topics like public finance management, socio-economic development, climate-smart policy, and governance reforms.
FAQ
Post Category
- RAS Salary
- Result
- RAS Admit Card
- RAS Job
- RAS Cutoff
- Preparation Tips
- RAS Answer Key
- RAS Exam Analysis
- RAS Syllabus
- RAS Previous Year Papers
- RPSC RAS Exam Pattern
- RAS Interview
- RAS Mains Exam Date
- RAS Vacancy
- RAS Test Series
- RAS Best Books
- RAS Preparation Resources
- RAS Coaching Centre
- History
- Polity
- Geography
- Economics
- Science
- Art and Culture
- RPSC RAS Application Form
- RPSC RAS Notification
RASonly Interview Guidance Program

Mr. Ashok Jain
Ex-Chief Secretary Govt of Rajasthan
- IAS officer of the 1981 batch, Rajasthan cadre.
- Passionate about mentoring the next generation of RAS officers with real-world insights.
- Got retired in Dec 2017 from the post of Chief Secretary of the state of Rajasthan.

Mr. Guru Charan Rai
Ex-ASP / SP in Jaisalmer
- Guru Charan Rai, IPS (Retd), retired as Inspector General of Police (Security), Rajasthan, Jaipur in 2017.
- Served as ASP and SP in Jaisalmer, Nagaur, Sri Ganganagar, Sawai Madhopur, Dausa, Sikar, and Karauli.
- He also held key positions as DIGP and IGP in the Law and Order division.

Mr. Rakesh Verma
Ex-IAS Officer, B.Tech, MBA, and M.A. (Economics)
- IAS officer of the 1981 batch and retired in Chief Secretary Rank.
- Civil servant of high repute and vast experience.
- Has been teaching UPSC CSE subjects for the last six years.
Related Post
Daily Current Affairs for RAS Exam Preparation 2026

Rajasthan Budget 2026–27 Focuses on Youth Jobs, Skills and...
February 13, 2026
Rajasthan Pushes Public-Centric Governance under Viksit Rajasthan@2047
February 13, 2026
Jaipur to Host District-Level Amla Buyer–Seller Conference
February 13, 2026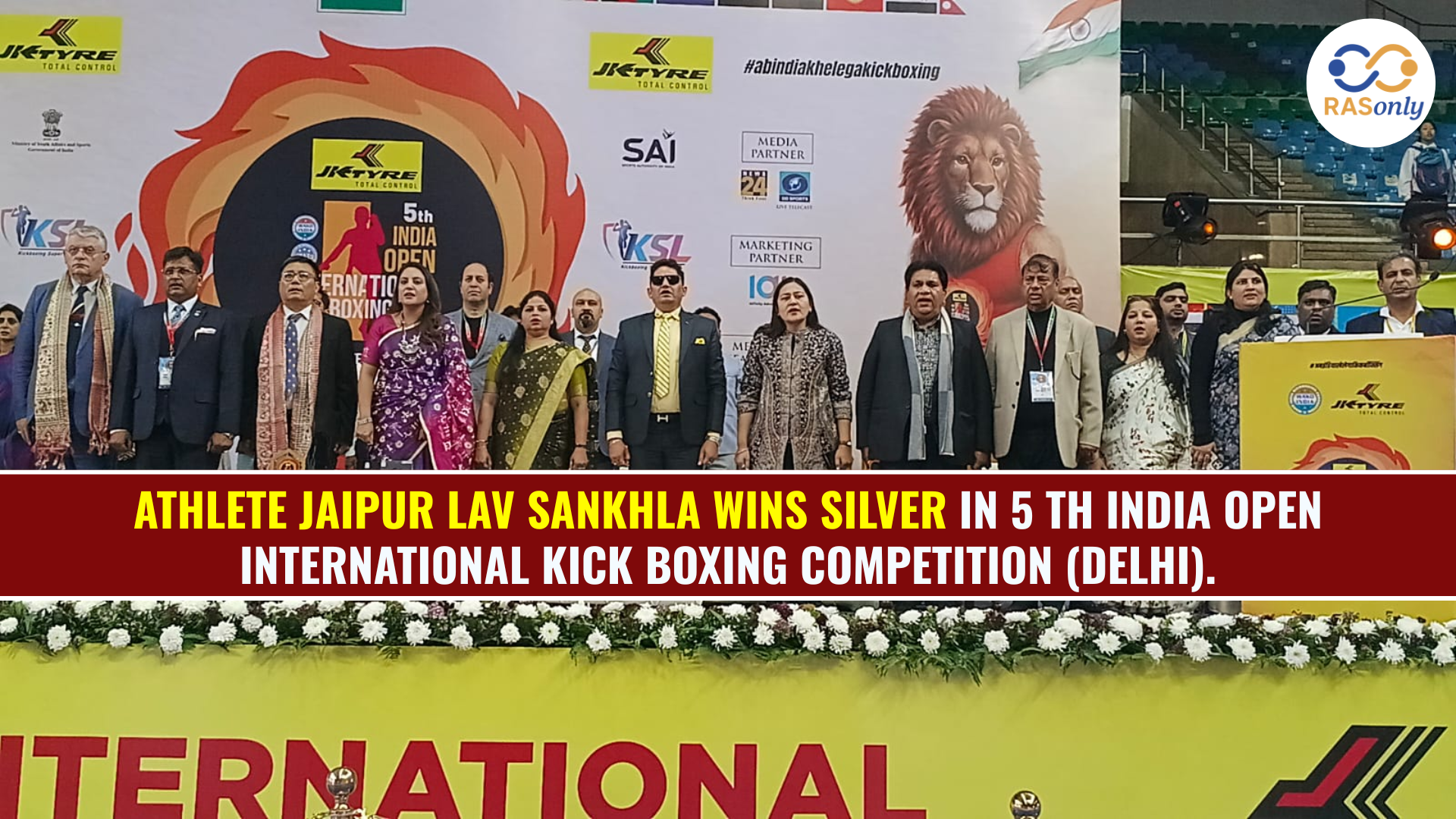
Lav Sankhla Wins Silver at India Open Kick Boxing
February 12, 2026👉🏻 Register Today to Join Classes! 👍🏻
- Team RASOnly -
🎯 Benefits of RASOnly Coaching:
- ✅ 1:1 Mentorship with RAS Officers
- ✅ Experienced and Expert Faculty
- ✅ Free Library Access
- ✅ Daily Minimum 4 Hours Must
- ✅ Comprehensive Study Material
- ✅ Regular Tests & Performance Analysis
- ✅ Personalized Guidance & Doubt Solving
- ✅ Online & Offline Class Options
- ✅ Affordable Fees with Quality Education
Key Highlights:
- 👉🏻 3-Day Refund Policy
- 👉🏻 New Batch Starting from 04 August
- 👉🏻 Registration Amount: Only ₹1000








